New in Nessus: Elliptic Curve Cryptography with SSH

Cryptography is like finding and patching system vulnerabilities. Both are a race. In the former, the race is between mathematicians finding efficient, hard-to-reverse computations and opposing mathematicians solving hard numerical problems to defeat them. In the latter, the race is between IT and malicious actors who may find the vulnerabilities first to exploit them. The race in encryption is fueled by the exponential increase in computing power outlined by Moore’s law, constantly driving the algorithms we use toward obsolescence.
For a long time, the golden standard in strong cryptography was based on schemes using the result of multiplying two prime numbers.
Breaking the encryption requires finding two prime numbers that when multiplied together result in the original number, also called the integer factors of the large number. In 1985, Neal Koblitz and Victor Miller separately invented cryptography based on the difficulty of finding the discrete logarithm of a random elliptic curve.

This relatively new approach has the advantage of faster computation than integer factorization. It also provides equivalent security using smaller keys.
The result of Koblitz and Miller’s work is called elliptic curve cryptography (ECC). Numerical improvements in integer factorization like the Number Field Sieve have put traditional RSA-style algorithms at risk with even relatively large key sizes and make the faster computation and smaller key sizes of elliptic curve cryptography an attractive alternative.
If a mathematical technique can feasibly factor integers or find the discrete logarithm of an elliptic curve, then it can be used to reveal private keys and break the cryptography. Looking into the future, quantum computing puts ECC at a higher risk than RSA due to Shor’s algorithm. Shor’s algorithm is a theoretical quantum computing technique for efficiently computing discrete logarithms. To use our race analogy, the cars are getting superchargers. But, in the meantime, ECC is a more secure approach than RSA.
Tenable has just added support for the use of ECC algorithms in SSH for credentialed scans. It’s another tool to help customers stay ahead in the race.
New algorithms
The addition of elliptic curve adds three new algorithms for Diffie-Hellman key exchange, bringing the total to six.
|
Original DH Algorithms |
Current DH Algorithms |
|
|
Six new signing algorithms have also been added, bringing the total to thirteen.
|
Original Signing Algorithms |
Current Signing Algorithms |
|
|
Asymmetric cryptography (e.g., RSA, DSS or ECC) generally serves three roles in SSH:
- Key exchange
- Authenticating clients to hosts
- Authenticating hosts to clients
Key exchange use can be broken down into encrypting the process of generating a shared secret (in this case, Diffie-Hellman) and the process of cryptographically validating the integrity of the key exchange messages. Getting Nessus® to use the new algorithms for these processes just means configuring the SSH servers on the scan targets to enable them, and configuring the corresponding credentials in the scan policy.
Scanning with ECC
Using the new algorithms for authentication requires reconfiguring the SSH credential configuration in your scan policy, so I will briefly touch on it here.
Client authentication
Nessus supports two forms of client authentication using cryptographic keys:
- The first is public key authentication, where a key pair is generated for each scanner and the public key for each pair is sent to the SSH servers.
- The second is certificate authentication (CA), which follows the same idea, but makes it easier to manage the server side by having each scanner’s public key cryptographically signed by a certificate authority key or CA. The advantage is that a server only has to be configured to trust the CA to authenticate any client possessing a certificate signed by that CA.
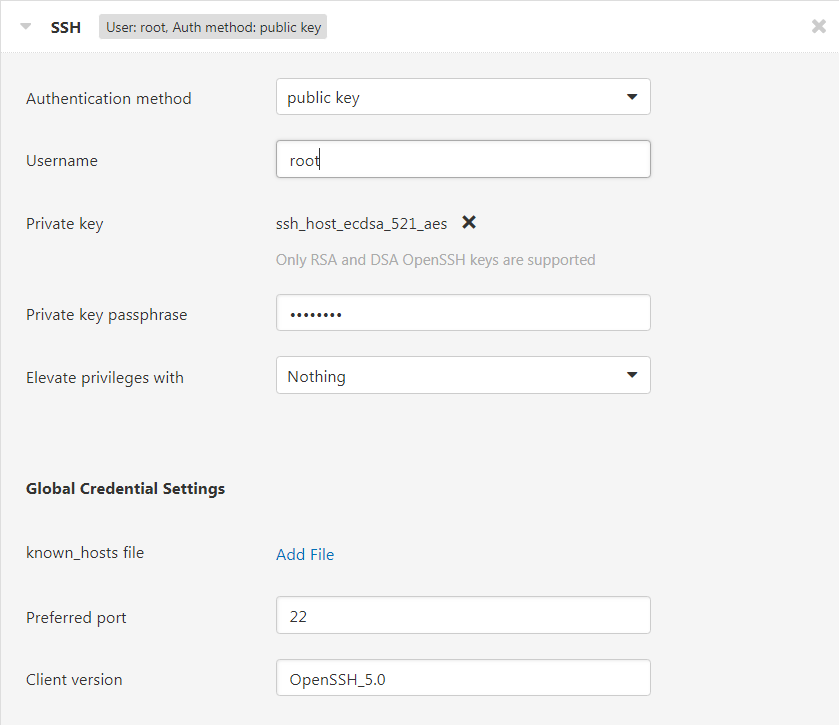
To use public key authentication, simply add the scanner’s own private key to the SSH credentials. The private key contains a copy of the public key, and only the public key will ever be sent across the network for authentication. Nessus uses the private key to cryptographically sign the authentication messages in a way that an SSH server can use to verify that the message wasn’t tampered with in transit. The credential configuration then looks like this:
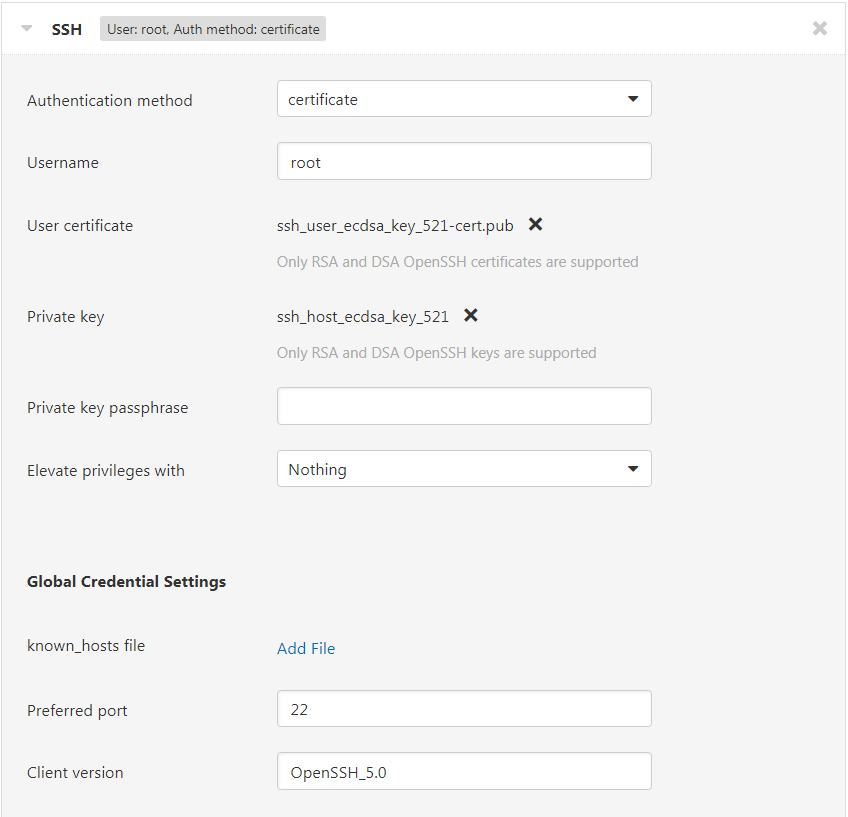
To use the new credential authentication method, create a trusted CA key pair for your scan targets. Then, sign the public key of your scanner’s key pair with the CA. Using OpenSSH, the command might look something like:
ssh-keygen -s ca_user_key_ecdsa_521 -n user1,user2,user3 -I a_certificate_name ./ssh_user_ecdsa_521.pub
This will produce a certificate named “ssh_user_ecdsa_521-cred.pub”. Your SSH credential will now require both the certificate and scanner’s private key. See below:
Host authentication
In addition, Nessus can use asymmetric cryptography to authenticate SSH servers. This is also called known host verification. It means Nessus will verify the identity of an SSH server. Here, the roles are reversed. Key pairs are generated on the scan targets, with Nessus configured to recognize them using a “known hosts” file. The public key of each scan target is placed in the “known hosts” file on a separate line. The file is uploaded as a part of the SSH credential global settings. Here’s an example:
your-host.your.domain.com ecdsa-sha2-nistp521 AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNoYTItbmlzdHA1MjEAAAAIbmlzdHA1MjEAAACFBAHR4cqH8yZbXVOSPSdOBUhIkELzANlgWOkNcdWZrRq95lglrf1ILe5Q0jukTKgjt413ie0TTKsTYG1nwaFJxKdRqAFw1NAGJxz3eVaf/6SN3kadNtcyPIPy5SbCF++G6iqhN1TuXenoXjwspCn3yWdiXF5rDoR5dDCLSMjJgH9tQaFanQ==
your-host2.your.domain.com ecdsa-sha2-nistp384 AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNoYTItbmlzdHAzODQAAAAIbmlzdHAzODQAAABhBP20zV8o3Ui4xSM0+3R/VtozwyzJXeurOirgvK3jWifV3/Re9XU/ZUeSeZBgDBdsvSQ+ym+At6CNU5o2Q9jUhHVSYo5tzYrS/pvD2uDykvy9M2oGG9XdxvWh5CrEbQRA0g==
@revoked your-host3.your.domain.com ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNoYTItbmlzdHAyNTYAAAAIbmlzdHAyNTYAAABBBLEPTqn+R5BsCTy8Qvq+Fga/pflGdeH0GHnksLlE65MiWOKWc4WvFuscS0wYVIWSLzrq3g+q739pz3j9HbgO10I="
Certificate-based known hosts verification is also supported. A CA key pair is generated for Nessus scanners to trust. Each scan target sends the public part of its host key to the scanner to be signed by the CA. The signed certificate is sent back to the scan target to be used in the host authentication part of the protocol exchange. The known hosts file used by Nessus becomes much simpler. It now contains a single line with the public key of the CA (see below):
@cert-authority *.your.domain.com ecdsa-sha2-nistp384 AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNoYTItbmlzdHAzODQAAAAIbmlzdHAzODQAAABhBJCQqR5NFoGJ8olau6CR3eOg0QZau0H2a4Li+ABmIYVgPscd2VhjBWE3N6WbMiWVk9dCy8Ih+rV62tsA9XbzgzUX0fw+ICkMP0ZlD8ER9MtfRoK4a8hOiy8IoMxORarZaA==
Not the end: Cryptography study will continue
Cryptography is complex. The mathematics are esoteric, and the legal and political realities surrounding cryptography are just as knotty.
ECC will be relevant for some time yet. Shor’s algorithm will theoretically require a quantum computer with 2,330 qubits to crack an elliptic curve with a 256-bit modulus. Putting that in context: Last year, IBM announced a quantum CPU featuring 17 qubits, with the prospect of 50 qubits on the horizon. At least one researcher believes that larger quantum computers may not even be possible.
The rise of IoT has driven recent interest in ECC due to the superior protection offered by smaller keys. This is a critical advantage in small devices with limited storage.
Nevertheless, ECC has proved more problematic and more prone to security flaws than integer factorization cryptography. Certain elliptic curves are degenerate, such as elliptic curves over a binary field or over primes. There’s also speculation that other classes of degenerate curves may exist. ECC in practice has been sensitive to the quality of the underlying system’s random number generator and vulnerable to side-channel attacks.
So, this isn’t the end of the story, but it’s all I have for now. At Tenable, we’ll keep studying cryptography and working to keep you ahead in the race.
相关文章
- Nessus







